2023 Enhancing Hydrophilicity of Thick Electrodes for High Energy Density A…
페이지 정보

본문
Abstract
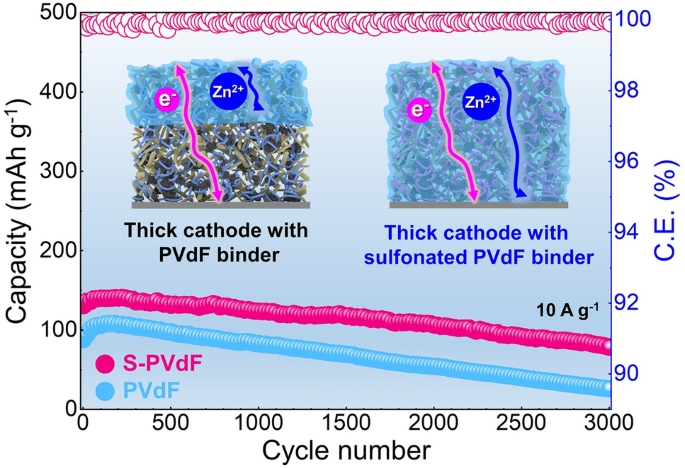
Thick electrodes can substantially enhance the overall energy density of batteries. However, insufficient wettability of aqueous electrolytes toward electrodes with conventional hydrophobic binders severely limits utilization of active materials with increasing the thickness of electrodes for aqueous batteries, resulting in battery performance deterioration with a reduced capacity. Here, we demonstrate that controlling the hydrophilicity of the thicker electrodes is critical to enhancing the overall energy density of batteries. Hydrophilic binders are synthesized via a simple sulfonation process of conventional polyvinylidene fluoride binders, considering physicochemical properties such as mechanical properties and adhesion. The introduction of abundant sulfonate groups of binders (i) allows fast and sufficient electrolyte wetting, and (ii) improves ionic conduction in thick electrodes, enabling a significant increase in reversible capacities under various current densities. Further, the sulfonated binder effectively inhibits the dissolution of cathode materials in reactive aqueous electrolytes. Overall, our findings significantly enhance the energy density and contribute to the development of practical zinc-ion batteries.
관련링크
- 이전글Digital-Twin-Driven Diagnostics of Crack Propagation in a Single LiNi0.7Mn0.15Co0.15O2 Secondary Particle during Lithium Intercalation 24.04.17
- 다음글A Bis(2-fluoroethyl) Carbonate as a New Electrolyte Additive for Enhancing the Long-Term Cycle Performance of Li-Metal Batteries 24.04.17
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.

