The effects of a solid electrolyte interface (SEI) additive, triacetoxyvinylsilane (VS), on the electrochemical performance of a lithium metal secondary battery were investigated. When  VS was added to the electrolyte, no lithium dendrite on the lithium metal surface after precycling was observed and thereby the lowest interfacial resistance of the unit cell
VS was added to the electrolyte, no lithium dendrite on the lithium metal surface after precycling was observed and thereby the lowest interfacial resistance of the unit cell 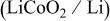 could be achieved. With these reasons, the capacity of the unit cell based on the electrolyte containing
could be achieved. With these reasons, the capacity of the unit cell based on the electrolyte containing  VS could maintain about 80% of the initial capacity after
VS could maintain about 80% of the initial capacity after  at a high charge/discharge current density (C/2,
at a high charge/discharge current density (C/2,  ).
).
2007 Effects of Triacetoxyvinylsilane as SEI Layer Additive on Electrochemi…
페이지 정보

본문
Abstract
관련링크
- 이전글New Separators Based on Non-Polyolefin Polymers for Secondary Lithium Batteries 24.04.17
- 다음글Enhancement of the mechanical properties of PVdF membranes by non-solvent aided morphology control 24.04.17
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.

